IT-Security (Part 1): WebLogic Server and Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS)
IT security is popular in a way never known before! I love it!
If I discussed e.g. in a WebLogic Server workshop about that, I heard normally form administrators: That’s not my thing, forget it! But newly, everybody wants to know “how can we secure our data and our information?!” To be honest, you need to detect your application server that you are using, and if you are not able to use WebLogic Server security features, then this could be your problem.
WebLogic Server uses a security architecture that provides a unique and secure foundation for applications that are available via the Web. It is designed for a flexible security infrastructure and enabled to response the security challenges on the Intra- and Internet. We are able to use security capacity of WebLogic Server as a standalone feature to secure WebLogic Server and/or as part of a corporation-wide, security management system.
Overview
In order to achieve a satisfactory level of security, we have to design an integrated security policy: from lack of resources till the increasing complexity of IT systems. The elementary principles in IT security are Confidentiality and/or privacy, availability and integrity. Confidentiality and/or privacy mean information that has to be protected against unauthorized disclosure. Availability means services; IT system functions and information must be available to users when they need it. Integrity means data must be complete and unaltered. Therefore, we understand security policy as a policy that it covers protection objectives and broad-spectrum security measures in the sense of the acknowledged requirements of an organization.
Simple to say, security is the protection of information that needs to protected, from unauthorized access. IT security could be helped us through technology, processes, policies and training, so that we can be sure that data stored and secured in a computer or passed between computers is not compromised. Therefor data encryption is the first step in the direction IT-Security. In order to access to specific resources, user needs to provide (normally) his user name and password. Data encryption is the transformation of data into a form that cannot be understood without decryption key(s).
Security Challenges
In a world that we used to work with distributed IT-landscape, we face to with different challenges, e.g. network-based Attacks, heterogeneity on application layer from user interface till to application. It is really difficult to stay on a standard security level for all of team members of development team. We cannot awaiting all of application developers to be able develop solve the security challenges such as privacy, identity management, compliance, audit too. Another area is interfaces between application server and backend database.
A simple case is presented on the following diagram: most applications are multi-tiered and distributed over several systems. A client invokes an application or sends a request to server. This case presents how many systems are in transaction involve. We have to check all of critical points and interfaces: network-based attacks, user interface, application Server and so on.
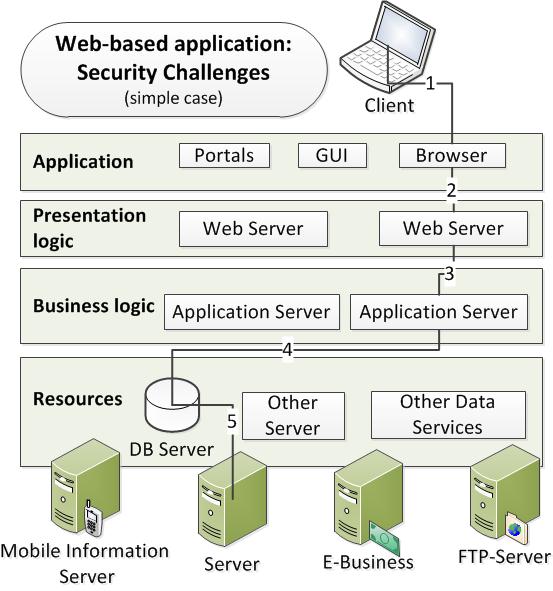
On these grounds, we need to use an enterprise security framework that allows application developers to pick and choose from a full set of reusable and standards based security services that allow security, privacy, and audit. Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) is a security framework that runs on WebLogic Server and is available as part of WebLogic Server. It combines the security features of BEA‘s internal security (WLS + Oracle Entitlement Server (OES)) and the OAS (Hava Platform Security (JPS) – earlier JAZN) to provide application developers, system integrators, security administrators, and independent SW vendors with a comprehensive security platform framework for Java SE and Java EE applications. In this form, Oracle is able to suggest a uniform enterprise security policy and a self-contained and independent framework with Identity management and audit services across the enterprise. The heart of whole system beats on WebLogic Server.
WebLogic Server provides authentication, authorization, and encryption services with which you can guard these resources. These services cannot provide protection, however, from an intruder who gains access by discovering and exploiting a weakness in your deployment environment. Therefore, whether you deploy WebLogic Server on the Internet or on an intranet, it is a good idea to contact an independent security expert to go over your security plan and procedures, audit your installed systems, and recommend improvements.
References
- See too: Do you forget your WebLogic Server password? No problem!, http://modj.org/did-you-forget-your-weblogic-server-password-no-problem
- Oracle Fusion Middleware 11.1.1.5, Security Guides http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E21764_01/security.htm
- Oracle® Fusion Middleware Understanding Security for Oracle WebLogic Server 11g Release 1 (10.3.5) http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E21764_01/web.1111/e13710/toc.htm
- Oracle® Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E21764_01/web.1111/e13707/toc.htm
- Oracle Platform Security Services 11gR1 (White Paper) http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/id-mgmt/opss-tech-wp-131775.pdf
- IT Security Guidelines, IT Baseline Protection in brief, Federal Office for Information Security

2 Antworten auf “IT-Security (Part 1): WebLogic Server and Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS)”